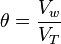|
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers (soil horizons) of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics. It is composed of particles of broken rock that have been altered by chemical and environmental processes that include weathering and erosion. Soil differs from its parent rock due to interactions between the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and the biosphere. It is a mixture of mineral and organic constituents that are in solid, gaseous and aqueous states.For other uses, see Soil (disambiguation). 
Surface-water-gley developed in glacial till, Northern Ireland 
Darkened topsoil and reddish subsoil layers are typical in some regions.
Water content or moisture content is the quantity of water contained in a material, such as soil (called soil moisture), rock, ceramics, fruit, or wood. Water content is used in a wide range of scientific and technical areas, and is expressed as a ratio, which can range from 0 (completely dry) to the value of the materials’ porosity at saturation. It can be given on a volumetric or mass (gravimetric) basis. Volumetric water content, θ, is defined mathematically as: where Vw is the volume of water and VT = Vs + Vv = Vs + Vw + Va is the total volume (that is soil volume + water volume + air space). Gravimetric water content is expressed by mass (weight) as follows: where mw is the mass of water and mb is the bulk mass. The bulk mass is taken as the total mass, except for geotechnical and soil science applications where oven-dried soil (ms, see the diagram) is conventionally used as mb. To convert gravimetric water content to volumetric water, multiply the gravimetric water content by the bulk specific gravity of the material. 
Soil composition by phase: s-soil (dry), v-void (pores filled with water or air), w-water, a-air. V is volume, M is mass.
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia : Soil, water and road construction (no earthmoving) |